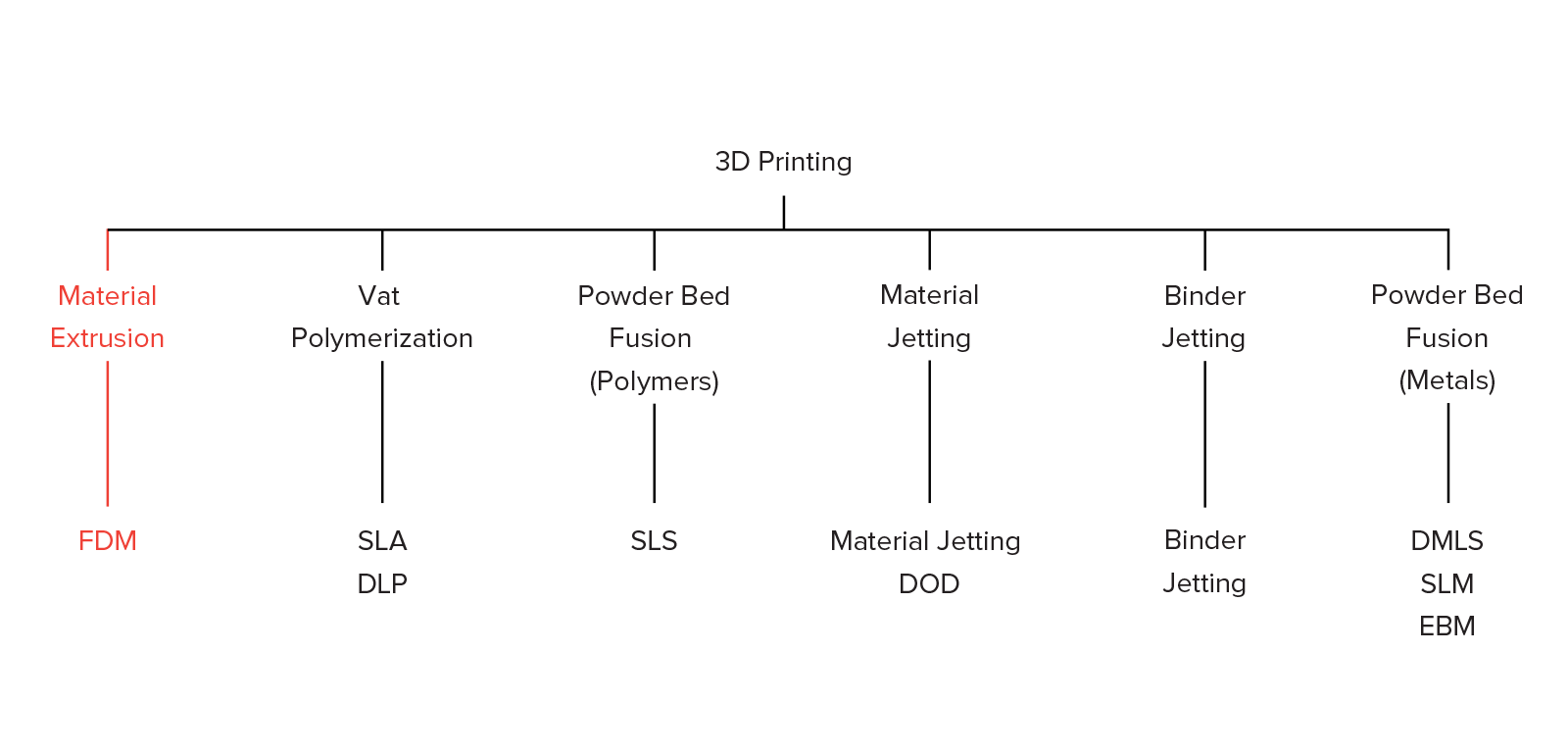
What is FDM 3D Printing?
FDM or Fused Deposition Modeling is an additive process for manufacturing that entails material extrusion. FDM is also commonly referred to as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF). In the process of manufacturing, an object is selected and a melted material is well dispersed inside the object with a pre-determined route in the form of layers followed by more layers. These materials can be used as thermoplastic polymers and are available in the form of a filament in the market. The largest proportion of 3D printing use is in the industrial sector. The global 3D printing market is said to rise by $41 Billion by the year 2026. Through this massive shift and economic growth, 3D printing is transforming every major industrial cooperation and leading the world to its advanced future.
3D printer was only considered suitable primarily for prototyping and one-off manufacture processes but today it constitutes a whole lot of every field you can name off. The use of FDM technology has always been trending in 3D Printing Industry. It presents largely installed bases of 3D printers universally. In this blog, all key principles and aspects of FDM are going to be elaborated in detail to give you an idea about the technology used in 3D printing with more clarity and brevity.
How does FDM work?
The FDM printing process
Here is how the FDM process functions:
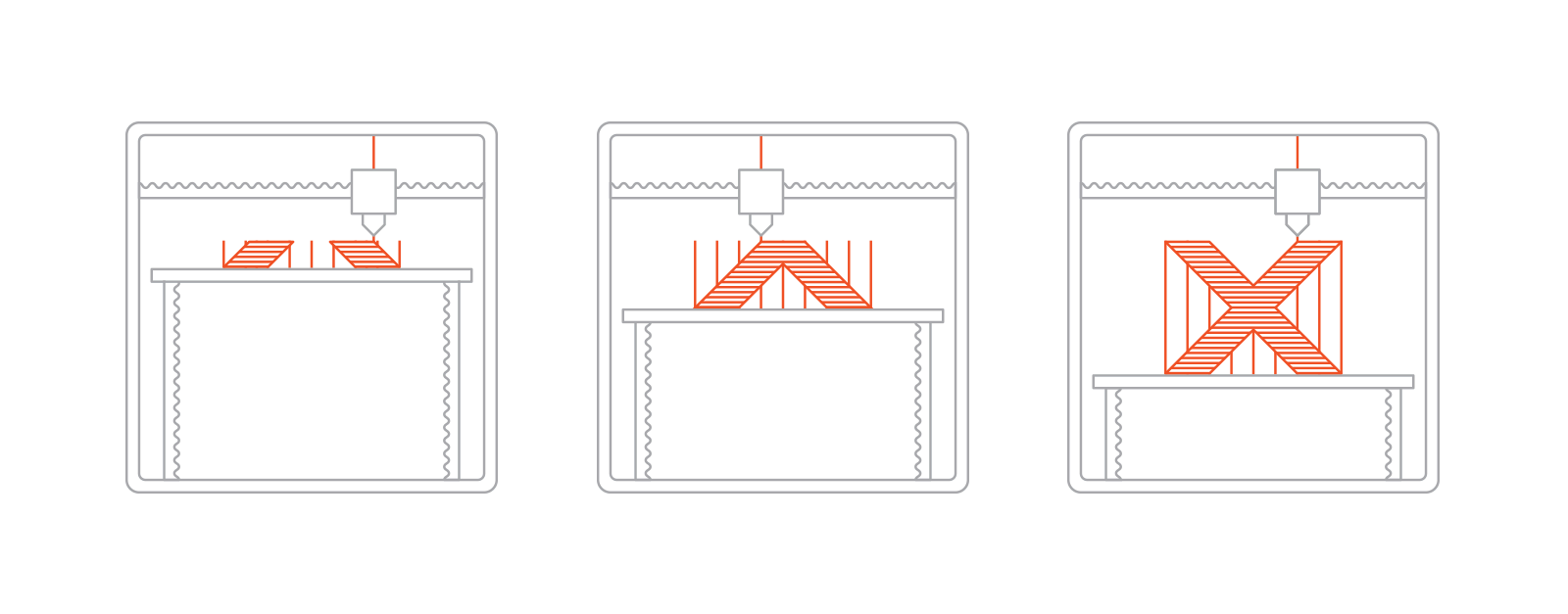
Typically, the process begins by spooling a thermoplastic filament into a 3D Printer. When the nozzle reaches the desired temperature, the filament is loaded to the head of the extrusion and the melting process starts.
The extrusion head is attached to a 3 axis system which allows it to move in 3-dimensional cross-section directions, the melted nozzle is extruded within the thin strands and is deposited layer after layer in already allocated positions and directions. Where it starts cooling and solidifies.
To fill in the area of the extrusion, multiple passes are needed. After finishing off a layer completely you can directly shift on to a new layer. The platform moves downwards and the extrusion head moves upwards. The same process is repeated for every layer. The process carries on until completion.
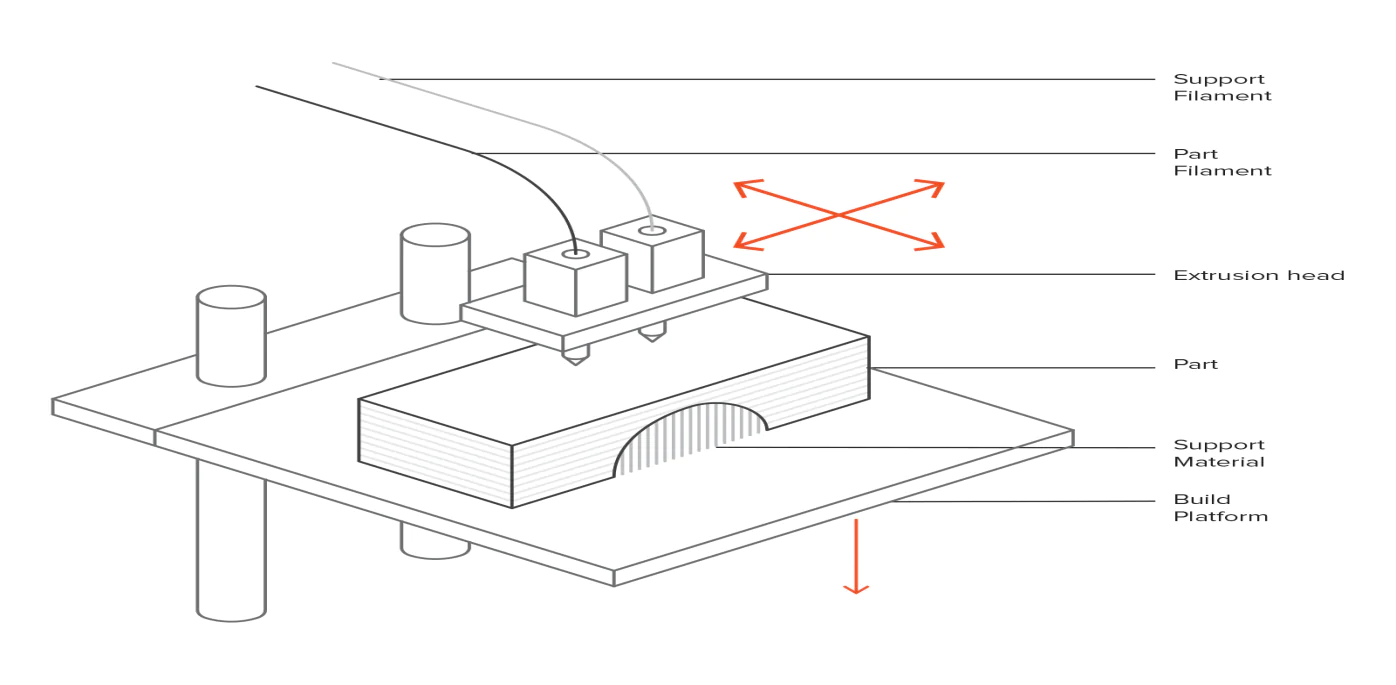
Schematic of a typical FDM printer
Characteristics of FDM
Most of the time, the FDM system allows the adjustment of different parameters. These parameters include setting up the temperature of both the nozzle and built platform. Other important parameters involve speed adjustment, height adjustment of the cooling fan, and the build platform. All such parameters are adjusted by designers and operators.
The build size of a 3D printer must be 200 x 200 x 200 mm. For industrial machines, the size must be as big as 1000 x 1000 x 1000 mm.
Warping
Warping is a common defect in FDM. Warping results in after cooling effect when the dimensions change with the rate of cooling effect at a different speed. Solidification followed by the decrease in dimensions causes it to warp. To reduce warping, the designers suggest the following actions:
Large flat areas: Large rectangular boxes are more exposed to warping and must be avoided as much as possible.
Thin protruding features: Protruding features are like prongs or forks and are much prone to warping. In such a case scenario, add some sacrificial material at the edge of a thin feature to avoid warping.
Sharp corners: Warping also occurs on rounded shapes. The addition of fillets can be of much help and good practice.
Different materials: Other materials such as ABS, PLA, PETG are generally more sensitive to warping and need special care to temperature transitions and a higher thermal expansion coefficient.
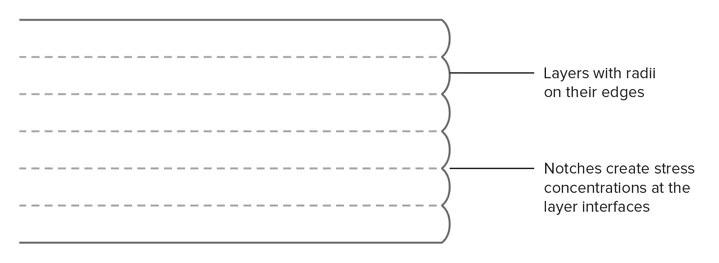
Layer Adhesion
Strong adhesion among the deposited layers is essential for FDM. It is because when a molten thermoplastic is extruded from the nozzle. The layers press against previous layers. Due to high pressure and temperature the surface of the initial layer re-melts. This results in the bond of layers with the new layer with the last printed layer.
Support Structure
The support structure is essential to create geometries in FDM. The melted thermoplastic can’t be deposited into thin air. The reason is that geometries need some support structure. The surface printed upon the support is low surface quality from any other portion. Hence, every part must be individually designed to minimize the support structure. Certain unique support liquids melt and blend and are used in industrial FDM 3D Printers. Printing provides support to enhance the surface quality of the overall design/object/model.
Infill & Shell Thickness
Parts of FDM are not usually printed in solid form. So is the case to reduce the print time and material cost. The outer perimeter is located by different passes called Shell. The inside is filled with a low-density structure called Infill. Infill and Shell are the preset parameters for FDM 3D Printing. For all desktop FDM Printers, 25% infill density is required and a thickness of 1 mm of the Shell is essential for a better comparison between strength and speed to print with a steady and faster speed.
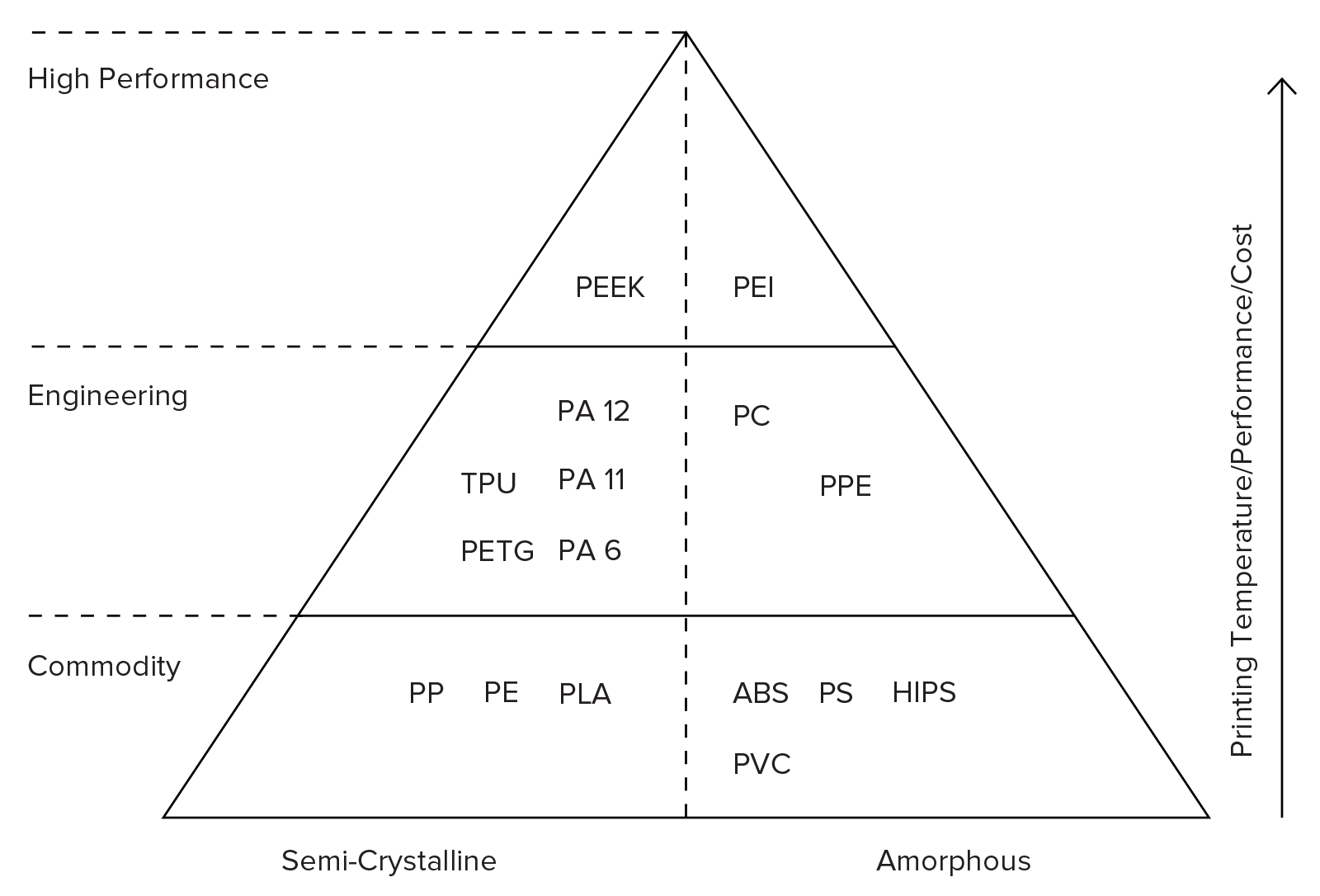
FDM Materials
The key strengths of FDM 3D Printing involve a wide variety of helpful materials. These range from engineering materials such as PA, PETG, and TPU to thermoplastics which include ABS and PLA. High-performance thermoplastics are also present which are PEEK and PEI.
Post Processing
FDM parts can be corrected with a very high standard by utilizing post-processing methods of FDM 3D Printing like sanding, priming, polishing, painting, cold welding, vapor smoothing, metal plating, and epoxy coating.
Benefits & Limitations of FDM
FDM 3D Printing involves many key benefits and other limitations of the technology as described as follows:
FDM is a very cost-effective solution for the industrial and manufacturing sectors. It produces customized thermoplastic printed parts and prototypes for your business advantage.
The leading times of FDM are comparatively short i.e. as quick as the next day delivery service.
A wide variety of thermoplastic materials is readily available for both prototyping and noncommercial applications.
FDM has the lowest dimensional resolution and accuracy as compared to 3D Printing. Therefore, it is suitable for portions with heavy fine and complex detailing.
FDM Parts consist of visible lines and layers hence, smoothing out around the edges post-processing is suggested.
FDM Parts are inherently anisotropic which makes up the layer adhesion mechanism.
How ITS can help you with 3D Modeling Service?
Information Transformation Service (ITS) has been providing 3D Modeling Services for over a time now. Information Transformation Services knows all about the modern-day industry and its trends in the Online Marketing Business. ITS is light on the budget and heavy in terms of quality and stature. Our highly responsive and interactive team specializes in 3D Product and Asset Modeling Services and will note down every essential detail provided by you and in return turn your dream into a real-life realistic or virtual reality. Information Transformation Service (ITS) also caters to a wide variety of services relating to efficient 3D Modeling and Designing services. If you are interested in ITS 3D Modeling Services, you can ask for a free quote!