How To Correct Lens Distortion
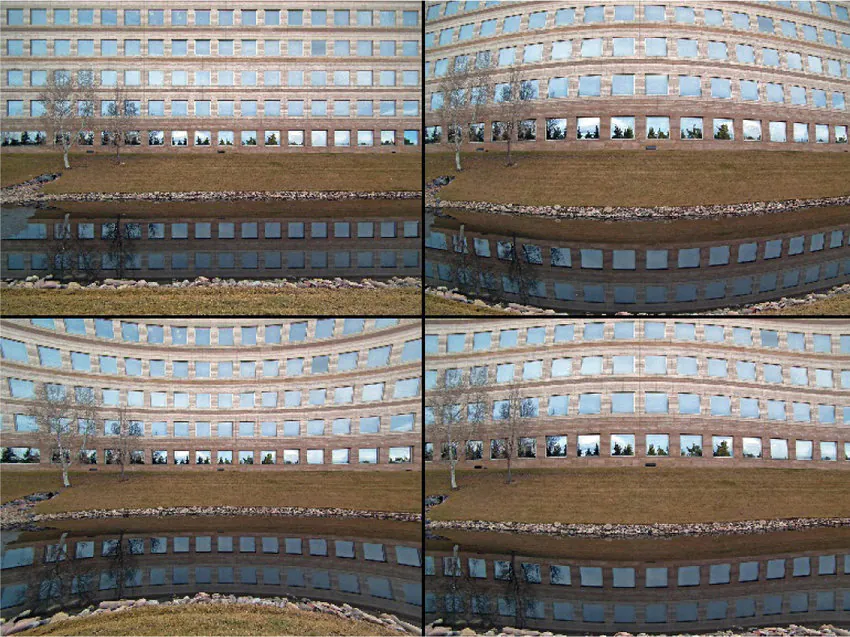
Lens distortion occurs when the optics of a camera lens produce certain image deformations, such as barrel or pincushion distortion, that can result in straight lines appearing curved or objects appearing stretched or compressed. These distortions can significantly impact photographs’ quality and accuracy, particularly when capturing architectural structures or geometrically precise subjects. However, many effective methods are available to correct lens distortion and restore the images to their intended appearance. Software tools like Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, and other image editing programs offer lens correction features that allow users to rectify distortions by applying specific algorithms tailored to various lens types. Specialized lens correction plugins and standalone applications provide automated or manual adjustments to counteract distortions. Understanding the nature of lens distortion and utilizing appropriate correction techniques empowers photographers to produce visually accurate and pleasing images.
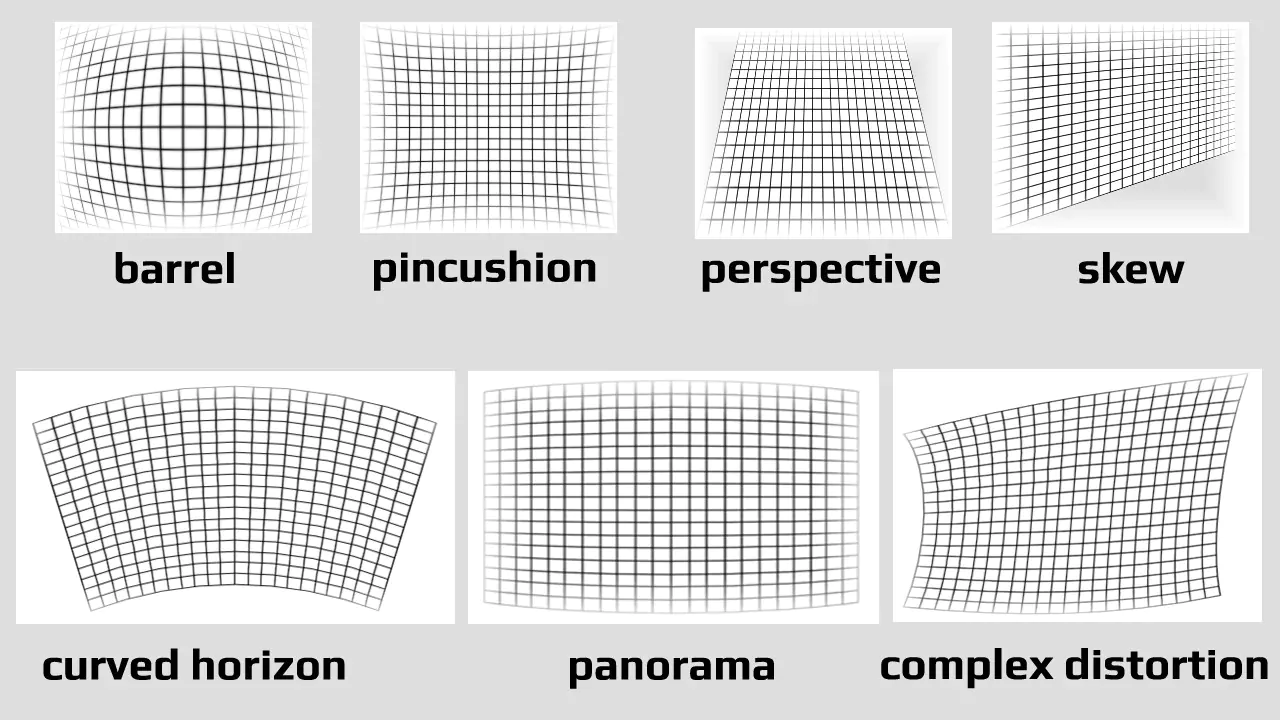
Types of Lens Distortion
Lens distortion can manifest in different forms, each with its unique characteristics. Common lens distortions are barrel, pincushion, mustache, and perspective.
Barrel distortion causes straight lines to appear curved outward, resulting in a bulging effect. Pincushion distortion, on the other hand, produces the opposite effect, making straight lines curve inward. Mustache distortion combines elements of both barrel and pincushion distortion, resulting in a wavy or undulating appearance. Perspective distortion occurs when the camera angle creates a sense of convergence or divergence, distorting the proportions and relationships between objects in the scene. Understanding various types of lens distortion is essential for accurately identifying and correcting them in post-processing.
Causes of Lens Distortion
Lens distortion can be caused by a combination of factors, including optical factors, lens design, focal length, and shooting distance. Optical factors such as lens aberrations and the quality of lens elements can contribute to distortion. Lens design plays a crucial role, as certain lens designs are more prone to specific types of distortion. Focal length can also influence distortion, with wider lenses often exhibiting more barrel distortion, while longer lenses may show pincushion distortion. Finally, shooting distance can impact distortion, with closer subjects often experiencing more pronounced distortions. Understanding the causes of lens distortion helps photographers make informed decisions and apply appropriate correction techniques.
Recognizing Lens Distortion in Photos
Recognizing lens distortion in photos requires a keen eye for details and an understanding its visual indicators. Straight lines that appear curved, such as a bowed horizon or bent architectural elements, are a common sign of barrel or pincushion distortion. Geometric objects may appear stretched or compressed, with circles appearing as ellipses. Faces and portraits can also exhibit distortion, with facial features appearing distorted or asymmetrical. Analyzing the overall geometry and proportions of the image can provide further clues. By developing a trained observation, photographers can accurately identify lens distortion and apply the appropriate correction techniques to restore the intended visual fidelity of their photographs.
Tools for Lens Distortion Correction
Photographers can access various powerful tools and software options for correcting lens distortion. These tools offer various features and capabilities that can effectively fix different types of distortion.
Adobe Photoshop:
Adobe Photoshop is a widely used image editing software offering several lens distortion correction tools. The “Lens Correction” filter allows users to correct common distortion issues automatically. The “Transform” tool also enables manual correction by manipulating perspective and straightening lines.
Adobe Lightroom:
Adobe Lightroom is a comprehensive photo editing and organizing software with lens correction features. The “Lens Correction” panel provides automatic correction using built-in lens profiles. It also offers manual adjustments to fine-tune distortion correction. The “Upright” tool corrects perspective distortion, which is especially useful for architectural photography.
Third-Party Plugins and Software:
Numerous third-party plugins and standalone software specialize in lens distortion correction. Here are a few popular options:
DxO OpticsPro: This software features an extensive database of lens profiles and offers automatic distortion correction based on specific lens models.
Capture One Pro: Along with its powerful RAW processing capabilities, Capture One Pro includes lens correction tools that allow users to correct various types of distortion and apply lens-specific adjustments.
PTLens: PTLens is a standalone application designed explicitly for lens distortion correction. It offers automatic correction based on lens profiles and manual adjustments for precise control.
Online Lens Correction Tools
Several online tools and websites provide lens distortion correction capabilities without installation. These tools allow users to upload images and apply automatic or manual corrections. They can be convenient options for quick fixes on the go.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of these tools may vary depending on the complexity and severity of the distortion. While automatic correction using built-in lens profiles can yield good results in many cases, manual adjustments provide more control and customization options for challenging distortions.
Selecting the appropriate lens profile or manually inputting the correct parameters is essential when using these tools. Lens profiles contain specific correction data for different lenses and focal lengths. By choosing the right profile or inputting accurate values, the software can accurately compensate for the lens distortion in your images. It’s worth noting that while these tools can significantly improve image quality, they may not eliminate all distortions, particularly in extreme cases. In such situations, manual adjustments and artistic interpretation may be necessary.
Manual Correction Techniques
Manual correction techniques provide photographers with precise control over lens distortion correction. While automated tools can be effective, manual adjustments allow for fine-tuning and customization to achieve the desired results.
Grid and Mesh Distortion: Using grid overlays or mesh transformations in photo editing software, photographers can manually adjust the distortion by manipulating control points. Grid overlays help align straight lines, while mesh transformations allow for more localized adjustments.
Perspective Adjustment: Perspective distortion occurs when the camera angle creates convergence or divergence, distorting the proportions and relationships between objects in the scene. Manual perspective adjustment tools like Adobe Photoshop allow photographers to correct vertical and horizontal perspective, straightening lines and correcting distortion.
Content-Aware Fill and Clone Stamp: In cases where lens distortion causes unwanted elements or stretching in specific areas, tools like Content-Aware Fill and Clone Stamp can be utilized. Content-Aware Fill intelligently replaces distorted regions with content similar to the surrounding area. At the same time, the Clone Stamp tool allows for the precise copying of pixels to cover up and correct distortions.
Localized Distortion Adjustment: Certain areas of an image may exhibit more pronounced distortion than others. Photographers can apply localized distortion adjustments by selecting specific regions or using masks. That allows for targeted corrections in areas that require more attention while leaving other parts of the image untouched.
Working with high-resolution images and zoom in for precise adjustments is crucial when applying manual correction techniques. Using software features like grid overlays and magnification tools helps ensure accurate correction. Maintaining a natural-looking result by avoiding overcorrection is essential, which can lead to artificial-looking or warped images.
While manual correction techniques require more time and effort compared to automated methods, they offer the advantage of total control and customization. Photographers can fine-tune every aspect of the correction process, producing images that accurately represent the intended scene while preserving the artistic vision.
Automated Correction Methods
Automated correction methods provide a convenient and efficient way to correct lens distortion, especially when dealing with many images or when time is limited. These methods utilize software algorithms and built-in lens profiles to automatically analyze and correct distortion.
Lens Profiles: Many photo editing software, such as Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom, have built-in lens profiles. These profiles contain specific correction data for different lenses and focal lengths. By selecting the appropriate lens profile for the image, the software can automatically apply the necessary corrections to counteract the distortion. This method ensures accurate and consistent results across multiple images.
Automatic Distortion Correction: Some cameras have in-camera automatic distortion correction features. The camera automatically applies correction algorithms to counteract known lens distortions when enabled. That can be especially useful for photographers who prefer to have their images corrected immediately, reducing the need for post-processing adjustments.
Artificial Intelligence Solutions: Artificial intelligence (AI) advancements have led to development of sophisticated distortion correction tools. These AI-powered solutions utilize machine learning algorithms to automatically analyze and correct lens distortions. These tools can provide accurate and efficient correction results by learning from vast datasets of lens profiles and distortion patterns.
When using automated correction methods, it’s essential to ensure that the correct lens profile or camera settings are selected. That provides that the software applies the appropriate corrections specific to the lens for capturing the image.
While automated correction methods offer convenience, it’s important to note that they may not always produce perfect results, especially in complex or extreme distortion scenarios. Some distortions may require additional manual adjustments or artistic interpretation to achieve the desired outcome. Photographers should also be mindful of potential trade-offs when using automated correction methods. Depending on the software or camera, slight compromises in image sharpness or other image characteristics may exist. Therefore, reviewing and assessing the corrected images is recommended.
Conclusion
Lens distortion is a typical challenge photographers face, but with the proper techniques and tools, it can be effectively corrected to achieve visually accurate and pleasing images. Whether you prefer manual adjustments or automated correction methods, software applications like Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom, as well as third-party plugins and standalone software, offer a wide range of options to correct lens distortion. By understanding the different types and causes of lens distortion, recognizing them in your photos, and employing the appropriate correction techniques, you can enhance the quality of your images and produce visually stunning results.