How Can I Create 3D Models For Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a rapidly expanding field that provides users with a genuinely immersive experience. The ability to explore and interact with a 3D virtual world sets VR apart from other forms of media. The success of VR depends largely on the quality of the content, which is why creating 3D models for virtual reality is such an important aspect of the development process. Creating 3D models for virtual reality requires a combination of artistic skill, technical knowledge, and creativity. In this blog, we will look at the steps involved in creating 3D models for virtual reality and the tools that can be used to achieve this.
Step 1: Plan and Conceptualize
Before beginning the actual process of creating 3D models, having a clear plan and concept in mind is essential, including defining the model’s purpose, the level of detail required, and the overall style of the model.
A crucial aspect of this stage is understanding the technical requirements of the VR platform on which the model will be used. That includes the polygon count, texture resolution, and file format. Each VR platform has unique technical requirements that must be considered when creating 3D models.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tools
Creating 3D models for virtual reality requires specialized software capable of handling the high level of detail required for VR. Some of the most popular 3D modeling software used in the industry include Blender, Maya, 3ds Max, and ZBrush.
Overall, the choice of software ultimately comes down to personal preference and the project’s specific requirements. Blender is popular for indie developers and small studios due to its open-source nature and powerful feature set. Maya and 3ds Max are industry-standard software larger studios use and offer a comprehensive set of tools for creating complex 3D models. ZBrush is primarily used for sculpting high-resolution models and is a favorite among character artists.
Step 3: Create the 3D Model
Once the plan and tools are in place, it’s time to create the 3D model. That involves creating a 3D mesh, adding textures, and applying materials to the model.
The first thing is to create a 3D mesh, the model’s basic structure that defines its shape and form. The mesh is created using extrusion, sculpting, and polygon modeling tools. The level of detail in the mesh depends on the project’s specific requirements.
Once the mesh is complete, the next step is to add textures to the model. Textures add surface detail to the model and can create various effects such as roughness, shininess, and transparency. Textures can be created using software such as Substance Painter or Photoshop.
Finally, materials are applied to the model. Materials are used to define how light interacts with the model’s surface and can be used to create various effects, such as reflective surfaces, transparency, and subsurface scattering.
Step 4: Optimize the Model for VR
Creating a 3D model for virtual reality is about more than just creating a high-quality model. It is also important to optimize the model for VR to ensure that it runs smoothly and efficiently.
One of the key considerations when optimizing a 3D model for VR is the polygon count. VR platforms have strict limits on the number of polygons that can be used in a scene. High polygon counts can cause performance issues and result in a suboptimal experience for the user.
Another consideration when optimizing a 3D model for VR is texture resolution. High-resolution textures can cause performance issues, especially on mobile VR platforms. It is important to balance texture resolution and performance to ensure that the model looks good without compromising the user experience.
The file format of the 3D model is also an important consideration when optimizing for VR. Some VR platforms have specific file formats that are optimized for performance. Choosing the correct file format for the target platform is important to ensure that the model runs smoothly and efficiently.
Step 5: Test the Model
Testing the model is crucial in creating 3D models for virtual reality. It tests the model on the VR platform to ensure that it runs smoothly and looks good.
During the testing phase, it is important to pay attention to things like the frame rate, the level of detail, and the model’s overall performance. Any issues identified during testing should be addressed before the model is released.
Step 6: Iterate and Refine
Creating 3D models for virtual reality is an iterative process. It is important to refine and iterate on the model until it meets the project’s specific requirements, which involves going back to the planning and conceptualization stage to identify improvement areas. It may also involve changing the mesh, textures, and materials to achieve the desired result.
The iteration process is important for creating high-quality 3D models that meet the project’s specific requirements.
The Eminent Tools for Creating 3D Models for Virtual Reality:
Blender
Blender is a free and open-source 3D modeling and animation software widely used in the gaming and animation industries. It offers various features for creating 3D models, including sculpting tools, UV unwrapping, and texture painting. Blender also has a built-in game engine that lets you preview your models in real-time, making it an ideal tool for creating 3D models for virtual reality.
Maya
Maya is a 3D modeling and animation software that is widely used in the film and gaming industries. It offers a range of features for creating 3D models, including advanced rigging and animation tools, particle and fluid simulations, and scripting capabilities. Maya also supports VR engines like Unreal and Unity, making it an ideal tool for creating 3D models for virtual reality.
3ds Max
3ds Max is widely used in the gaming and architecture industries. It offers various features for creating 3D models, including rigging and animation tools, procedural modeling, and support for VR engines like Unreal and Unity.
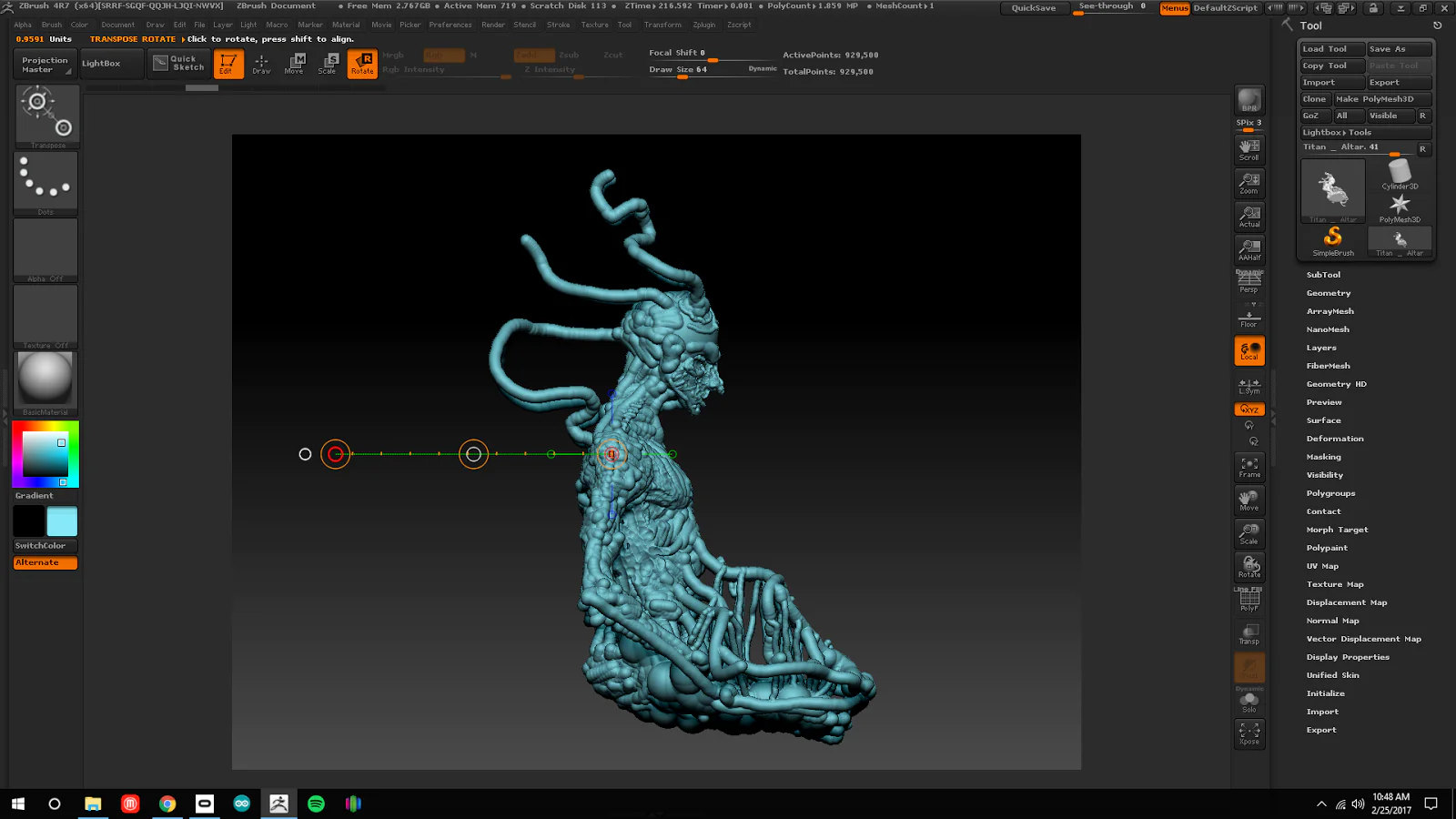
ZBrush
ZBrush is a digital sculpting software widely used in the film and gaming industries. It offers a range of features for creating highly detailed 3D models, including sculpting tools, poly painting, and support for VR sculpting. ZBrush is an ideal tool for creating highly detailed 3D models for virtual reality.
Substance Painter
Substance Painter is a 3D texturing software widely used in the gaming and animation industries. It offers many features for creating highly detailed and realistic textures, including a library of materials and textures, support for PBR workflows, and procedural texture generation tools. Substance Painter is an ideal tool for creating highly detailed and realistic 3D models for virtual reality.
Considerations for Creating 3D Models for Virtual Reality:
Optimize your models for VR
When creating 3D models for virtual reality, optimizing your models for VR platforms is important, which includes reducing the number of polygons, minimizing texture sizes, and ensuring that your models are optimized for the VR platform you are targeting. That will ensure that your models run smoothly and look realistic in VR.
Use PBR workflows
Physically Based Rendering (PBR) workflows are essential for creating 3D models that look and feel realistic in VR. PBR workflows consider the physical properties of materials, such as roughness and reflectivity, to create highly realistic textures that look and feel like real-world materials.
Use reference images
Reference images are essential for creating highly detailed and realistic 3D models, especially for virtual reality. They provide a visual guide for creating accurate proportions and textures and help ensure your models look and feel realistic in VR.
Practice good topology
Good topology is essential for creating 3D models that look and feel realistic in VR. Topology is how vertices, edges, and faces are arranged in a 3D model. Good topology ensures that your models deform properly during animations and look smooth and detailed in VR. When creating 3D models for virtual reality, practising good topology using edge loops, avoiding triangles, and minimizing the number of polygons is important.
Use VR headsets for testing
To ensure that your 3D models look and feel realistic in VR, testing them on VR headsets is important. Testing your models on VR headsets will give you a sense of the scale, perspective, and immersion of your models in VR. That will help you identify any issues with your models and make adjustments as necessary.
Learn from tutorials and online resources.
Learning how to create 3D models for virtual reality takes time and practice. Fortunately, many tutorials and online resources are available to help you get started. These resources cover various topics, from modeling and texturing to animation and rigging. By taking advantage of these resources, you can learn new techniques and improve your skills as a 3D artist.
Collaborate with other artists.
Collaborating with other artists can be a great way to learn new skills and techniques and get feedback on your work. By working with other artists, you can share ideas, learn from each other’s strengths, and push to create better, more immersive 3D models for virtual reality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, creating 3D models for virtual reality requires a combination of technical expertise and artistic skill. Using the right tools and following a well-defined process, you can create high-quality 3D models that look realistic in VR. Regardless of your level of expertise, many resources are available to help you get started and improve your skills. You can create immersive and memorable experiences for VR users with practice and dedication.