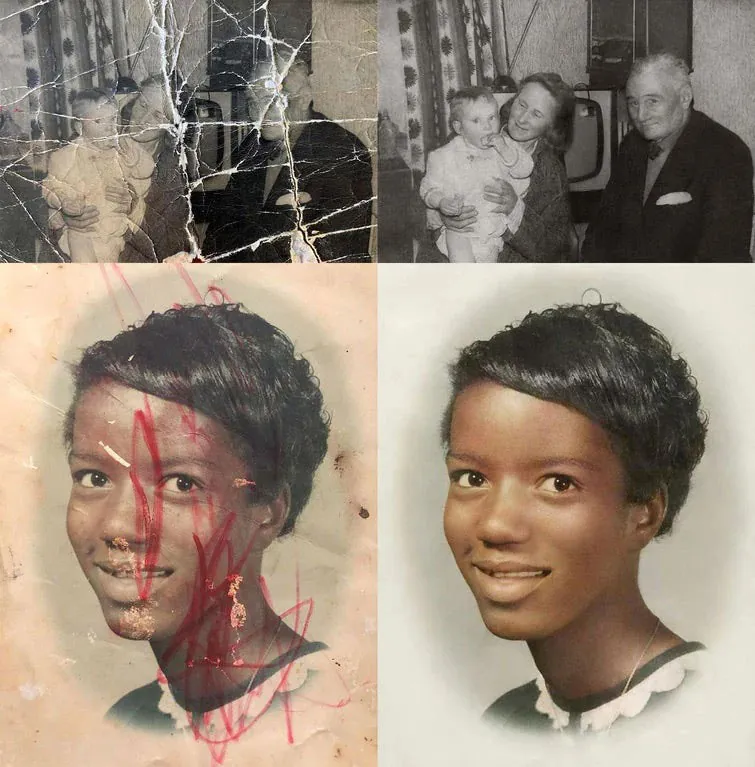
How To Restore Old And Damaged Photos
Restoring old and damaged photos is a fascinating process that allows us to preserve and revive cherished memories from the past. Over time, photographs can fade, develop cracks, or accumulate stains, diminishing their original quality. Photographs can lose some of their original quality over time due to fading, cracking, or staining. However, by virtue of improvements in digital restoration methods, it’s now possible to give these priceless pictures a fresh new look. Old and damaged images can be fixed, colors can be brought back to life, and missing details can be recreated using meticulous analysis, expert editing, and modern technological tools. This blog post will analyze the craft of photo restoration, revealing the methods that can restore these treasured pictures to their prior splendor.
Understanding the Importance of Photo Restoration
Old and damaged photos hold sentimental value as they capture moments and people from the past. They are visual links to our personal histories, connecting us to our ancestors, family members, and significant events. Preserving and restoring these photographs is crucial to safeguarding our heritage and ensuring that future generations can appreciate and learn from them. Photo restoration goes beyond fixing visual imperfections; it preserves and honors our collective memories.
Assessing the Damage: A Step-by-Step Approach
Before embarking on the restoration journey, it is crucial to assess the extent of the damage. Careful evaluation allows us to identify the types of deterioration, such as fading, discoloration, scratches, tears, or mold. By understanding the specific issues affecting the photo, we can develop a targeted restoration plan and choose appropriate techniques and tools.
Visual Inspection: Start by examining the photograph under good lighting conditions. Analyze for any visible signs of damage, such as stains, tears, or surface irregularities. Take note of areas where the image has faded, or details need to be included.
Digitization: To ensure the preservation of the original photo and facilitate restoration, creating a high-resolution digital copy is recommended. Scanning the image or capturing a high-quality photograph allows for easier manipulation and editing in the digital realm.
Detailed Analysis: Zoom in on the digital copy to assess the finer details of the damage. Pay attention to areas that require restoration, such as facial features, text, or intricate patterns. This analysis will guide the subsequent restoration process.
Essential Techniques for Photo Restoration
Photo restoration involves various techniques to repair and enhance the damaged image. Different approaches may be employed to achieve the desired results depending on the specific issues.
Repairing Tears and Scratches: Tears and scratches can significantly mar the appearance of a photo. Using the clone stamp tool or the healing brush tool in photo editing software, carefully clone or heal the damaged areas, matching them with the surrounding background or texture. This technique demands precision and attention to detail to ensure a seamless repair.
Color Correction and Enhancement: Photographs can lose their original colors, resulting in a faded or yellowish appearance. Color correction techniques, like adjusting the levels, curves, or color balance, can help restore the vibrancy and credit of the image. This process involves fine-tuning the color channels and tones to accurately reproduce the colors and recreate the intended atmosphere of the original photo.
Removing Stains and Discoloration: Stains, water damage, or discoloration due to mold or age can be challenging to remove. Techniques like spot healing, content-aware fill, or manual cloning can help eliminate these imperfections, restoring the photo’s original clarity. It is essential to take precautions to guarantee that the restoration is flawless and does not add any new artifacts or distortions.
Reconstructing Missing Details: In cases where significant portions of the image are missing or damaged, reconstruction techniques come into play. By carefully analyzing the surrounding areas and using reference points, skilled photo restorers can recreate missing details, such as facial features or background elements. This process often involves a combination of manual drawing and cloning to seamlessly integrate the reconstructed elements into the rest of the image.
Noise Reduction: Older photos often suffer from graininess or digital noise. Applying noise reduction techniques can help smooth out the image and improve overall quality. Noise reduction algorithms analyze the image and reduce unwanted noise while preserving important details. It is vital to establish a balance between noise reduction and maintaining the natural texture and sharpness of the image.
Sharpening and Detail Enhancement: Restored photos may benefit from sharpening and detail enhancement to bring out the finer elements and textures. This technique involves selectively enhancing edges and adding clarity to specific areas, which can significantly enhance the image’s overall sharpness and visual impact.
By combining these essential techniques, photo restoration can breathe new life into old and damaged photos, allowing us to rediscover their beauty and preserve their memories. It requires skill, patience, and an artistic eye to achieve optimal results while maintaining the integrity and authenticity of the original image. With practice and experience, one can master these techniques and create stunning restored photographs that honor the past and delight the present.
Leveraging Modern Software Tools for Photo Restoration
Photo restoration has been revolutionized by advancements in modern software tools, which provide powerful capabilities and intuitive interfaces for efficient and effective restoration processes. These tools leverage cutting-edge technologies and algorithms to assist in the restoration of old and damaged photos. Here are some of the critical software tools that can be leveraged for photo restoration:
Adobe Photoshop: Regarding editing and restoring photographs, Adobe Photoshop is the industry standard. It offers many tools and features that enable precise and detailed restoration work. The healing brush tool, clone stamp tool, and content-aware fill are just a few examples of the tools Photoshop provides for repairing damaged areas, removing blemishes, and reconstructing missing details. Photoshop also offers advanced color correction capabilities, including adjustment layers, curves, and selective color tools, allowing for accurate color restoration and enhancement.
GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program): GIMP is a free and open-source image editing software that provides a comprehensive set of tools for photo restoration. It offers features such as the clone tool, healing tool, and perspective clone tool, which help repair tears, scratches, and other forms of damage. GIMP also supports various color correction and enhancement techniques, making it a versatile tool for restoring old and damaged photos.
AI-Powered Restoration Tools: Artificial intelligence (AI) has recently made significant strides in photo restoration. AI-powered restoration tools leverage machine learning algorithms to repair and enhance images automatically. These tools can intelligently remove scratches, restore faded colors, and even reconstruct missing portions of the photo. They analyze vast amounts of data to learn from examples and apply restoration techniques that mimic the skills of professional photo restorers.
Dedicated Restoration Plugins: Many software plugins are designed for photo restoration. These plugins offer specialized tools and functionalities that streamline the restoration workflow. For example, plugins may provide automatic dust and scratch removal, noise reduction, or color restoration features. They often integrate seamlessly with popular image editing software, enhancing the capabilities of the existing tools.
When leveraging modern software tools for photo restoration, it is essential to go deeply through the features and techniques they offer. Each tool has its strengths and learning curve, so exploring tutorials, online resources, and user communities is beneficial to maximize the potential of these software tools. By harnessing the power of these tools, photographers and restoration enthusiasts can achieve remarkable results in restoring old and damaged photos with efficiency and precision.
Preserving and Protecting Restored Photos
Once the restoration process is complete, preserving and protecting the newly restored photos for future generations is crucial.
Archival-Quality Printing: If you plan to physically display or share the restored photos, opt for archival-quality printing materials and techniques to ensure long-term preservation.
Digital Backup: Create multiple digital backups of the restored images and store them in secure locations, like external hard drives or cloud storage platforms. That ensures that even if the physical copies are damaged or lost, the digital versions can be easily accessed and reproduced.
Handling and Display: When handling or displaying restored photos, use clean, dry hands and avoid touching the surface directly. Frame the images using acid-free materials and display them away from direct sunlight or extreme environmental conditions.
Learning and Growing as a Photo Restorer
Continuously learning and growing as a photo restorer is vital to honing your skills and achieving exceptional results. Immerse yourself in research, explore online tutorials, and enroll in courses that delve into restoration techniques and best practices. Regular practice is crucial for refining your abilities, so work on diverse projects to gain hands-on experience. Seek feedback and guidance from experienced restorers to improve your craft and expand your knowledge. Embrace emerging technologies and tools to stay updated with the latest advancements in the field. Learn from mistakes, analyze unsuccessful attempts, and adapt your approach accordingly. Cultivate an artistic eye by studying composition, lighting, and aesthetics. With dedication and continuous learning, you can evolve into a proficient and accomplished photo restorer, capable of breathing new life into cherished images.
Conclusion
In conclusion, restoring old and damaged photos allows us to rediscover and appreciate the beauty of our visual heritage. By understanding the importance of photo restoration, assessing the damage, employing essential techniques, leveraging modern software tools, and preserving the restored photos, we can ensure that these precious images continue to tell stories and evoke emotions for generations.