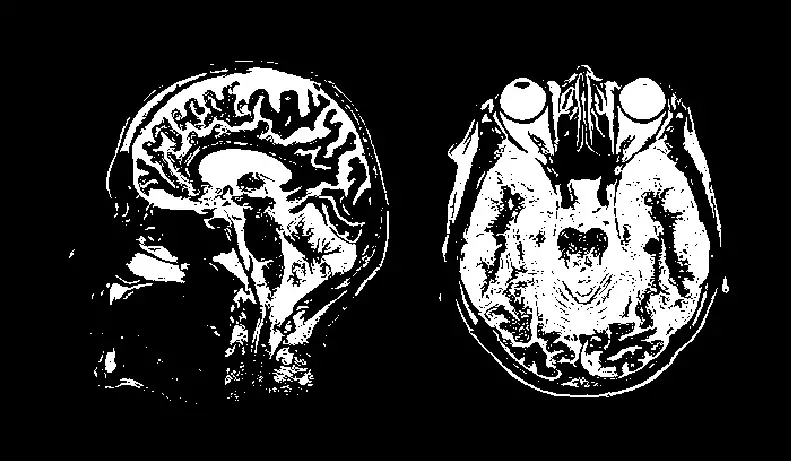
How To Apply A Threshold To Images
Splitting a picture into a foreground and background using image thresholding is an easy yet efficient method. By transforming grayscale photos into binary pictures, this image analysis technology separates different objects within an image. When it comes to images, the choice of high-contrast photos is the best candidate for this technique, and it can isolate desired chunks of the image to further modify or analyze. A number of thresholding forms are employed in image editing, though histogram and multi-level are the two most popular picture thresholding algorithms, which are excessively utilized by digital artists and image editors. Besides its general usability, the image threshold technique is also valuable in industries like medical imaging, satellite imagery, and environmental monitoring exertions. Thresholding is the best tool for researchers, engineers, and artists to extract useful data or features from shots for further inspection or manipulation. This blog will illustrate the strategies to embrace while applying threshold values in images from various imaging contexts.
Step 1: Image Examination
Decide the objective of thresholding the photo, whether upgrading highlights, sectioning objects, or analyzing data.
Select an image appropriate for the aiming purpose, guaranteeing it contains the fundamental highlights or components for successful thresholding.
Survey the photo’s properties, such as resolution, color profundity, and organization, to guarantee compatibility with the thresholding handle.
Assess the quality of the image to guarantee clarity and detail, which are significant for exact thresholding outcomes.
On the off chance that utilizing copyrighted or licensed, pictures guarantees compliance with utilization rights and consents.
Consider making a backup duplicate of the initial picture to protect data integrity and encourage experimentation without the chance of data misfortune.
Set up a conducive workspace with suitable software tools and assets for productive image processing.
Conclude the picture selection based on the specified criteria and availability for thresholding.
Step 2: Threshold Method Specification
Get yourself familiar with different thresholding strategies like global thresholding, adaptive thresholding, and Otsu’s thresholding.
Look into the properties of the image, including lighting conditions, noise levels, and contrast, to decide the most appropriate thresholding strategy.
Clarify the particular goals of thresholding, whether it’s double segmentation, including enhancement, or quantitative examination.
Evaluate the computational complexity and asset prerequisites of distinctive thresholding strategies to guarantee compatibility with accessible equipment and software.
Discover literature, tutorials, and expert recommendations to get the qualities, limitations, and applications of each thresholding plan.
Take into consideration the setting of the image, like its content, purpose, and expected audience, to select a thresholding strategy that aligns with the overall goals.
Conduct preparatory tests or simulations to compare the execution of distinctive thresholding strategies and select the most compelling approach for the given image and project.
Step 3: Grayscale Conversion

Decide if the image has to be converted to grayscale or another appropriate format for thresholding.
If the picture is in color or contains different channels, switch it to grayscale to simplify the thresholding process.
Within the case of multichannel images, consider holding particular channels that contain significant information for thresholding.
Guarantee that the conversion process holds the integrity of the image data and does not present artifacts or data loss.
If color data is protected, survey its pertinence to the thresholding task and appropriately alter the approach.
Affirm that the changed-over image is consistent with the chosen thresholding strategy and can successfully address the specified highlights or characteristics.
Retain track of the conversion process and any alterations made to the image format for future reference and reproducibility.
Step 4: Threshold Operation
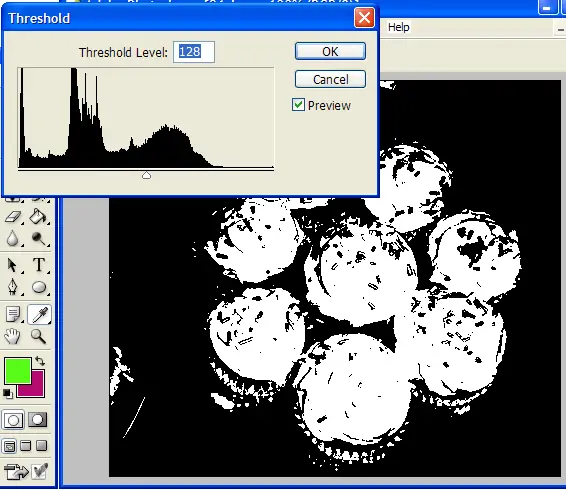
Select an introductory threshold value based on the image characteristics, such as intensity dispersion or visual inspection.
If you are utilizing global thresholding, apply the chosen threshold value consistently across the whole image to divide pixels into foreground and background.
For photos with shifting light or contrast, utilize adaptive thresholding strategies that alter the threshold locally to account for such varieties.
Consider applying Otsu’s automatic threshold selection strategy to decide an ideal threshold value founded on the image’s histogram.
Evaluate the adequacy of the applied threshold by visually reviewing the segmentation outcome and comparing it to the first picture.
If fundamental, refine the threshold value iteratively based on the visual input or quantitative assessment of the thresholding results.
Record the chosen threshold value and any alterations made amid the thresholding process for reproducibility and future reference.
Step 5: Values Adjustment
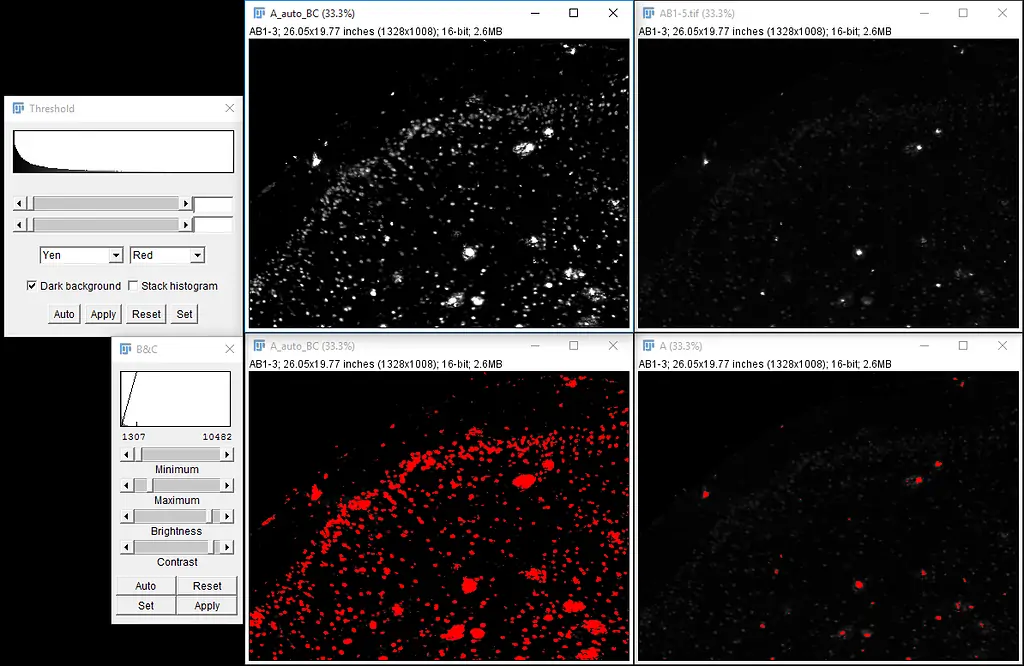
Scan the segmentation outcome with the chosen threshold value to distinguish regions of enhancement or refinement.
Analyze the photo’s histogram to get the conveyance of pixel intensities and distinguish potential thresholding challenges.
Take into consideration the particular characteristics of the image, such as contrast, noise, and illumination varieties, which may impact the choice of threshold value.
Incrementally alter the edge value based on observed segmentation results, aiming to attain a balance between foreground object separation and foundation noise suppression.
Screen the impact of threshold adjustments on the image division consistently through visual review, guaranteeing that vital highlights are satisfactorily highlighted.
Utilize histogram analysis methods, such as peak detection or valley identification, to distinguish optimal threshold values that maximize class separability.
Approve the effectiveness of threshold value alterations by comparing the refined segmentation results with the first image and desired division objectives.
Step 6: Image Analysis
Display the thresholded picture visually to observe the segmentation result and evaluate the effectiveness of the connected thresholding strategy.
Emphasize the zones classified as foreground or foundation based on the thresholding developments to distinguish between them visually.
Revise display settings such as brightness, contrast, and color mapping to improve the visibility of segmented regions and progress interpretability.
Overlay the thresholded image onto the initial image to encourage comparison and visualization of the segmentation process.
Give zoom and pan controls to empower a detailed review of particular regions inside the thresholded image, encouraging qualitative analysis.
Apply false color mapping methods to imagine intensity levels or segmented districts utilizing distinct color representations, improving clarity and interpretation.
Take screenshots of the visualized thresholded image for documentation, presentation, or advanced analysis purposes, guaranteeing reproducibility and sharing of results.
Step 7: Final Edits
Assess the quality of the thresholded image division in accomplishing the specified objectives, such as feature extraction or object separation.
Accomplish morphological operations, like erosion, dilation, opening, or closing, to refine the sectioned regions and progress their shape or connectivity.
To evaluate and characterize fragmented districts, extract relevant highlights from the thresholded image, such as object centroids, forms, or surface descriptors.
Allot unique names to segmented objects or regions to encourage identification, tracking, or measurement in consequent analysis tasks.
Execute edge detection algorithms to distinguish and highlight boundaries between segmented regions, empowering exact delineation of objects or structures.
Use post-processing filters, like noise reduction or smoothing filters, to further exalt the quality and clarity of the thresholded picture.
Record the applied further processing procedures and their parameters for reproducibility and future reference in consequent analysis or experimentation.
Conclusion:
In summary, thresholding is a critical tool in image editing, which can potentially isolate visual data and unveil masked patterns. Its role goes past image editing or photography, pervading fields varying from medical imaging to remote sensing and digital art, where it enables the isolation and enhancement of critical features within images. Eventually, thresholding serves as not only an image manipulation technique but a fundamental component that enfolds various industries, facilitating practitioners across occupations to unclose the dormant information and potentials ingrained within visual data. It results in extending learning, innovation, and visionary presentation.



