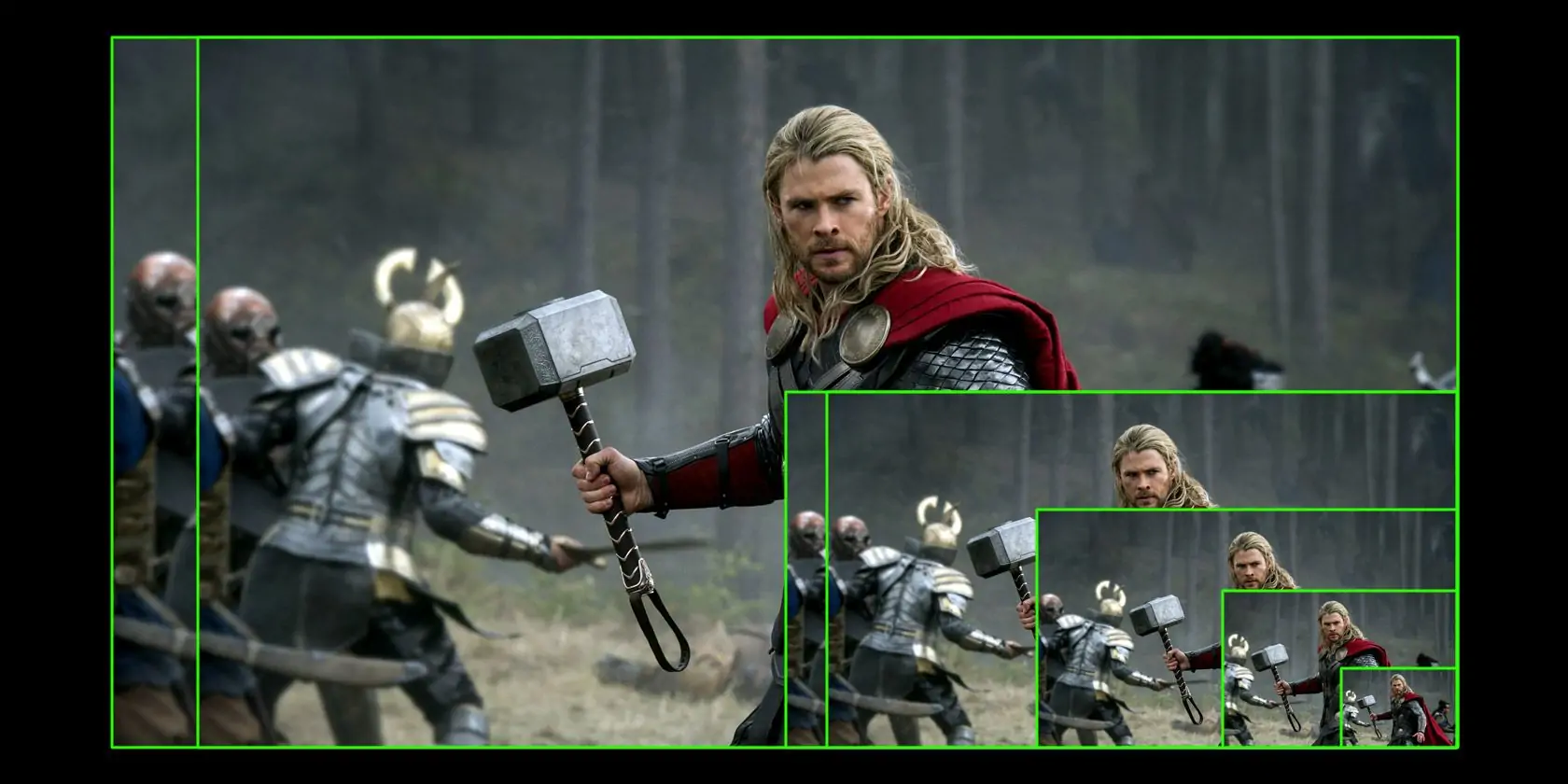

How To Do Image Upscaling
The process of Image upscaling is adopted to expand the resolution or size of images in such a way that the quality is preserved as much as possible. The upscaling strategy is often utilized in manifold areas, including video editing, photography, and digital illustrations. In this process, upscaling algorithms dissect the current pixels of the image and operate mathematical calculations to interpolate new pixels to fill in the gaps when increasing the image size. As a result, you can get a larger image that appears as similar to the initial one as possible, minimizing grimaces like blurriness or pixelation. Additionally, the evolved upscaling approaches possess efficient machine-learning algorithms that can foresee and yield high-quality attributes in the upscaled shot. You can employ editing software like Photoshop, GIMP, ON1 Resize, Topaz Labs Gigapixel AI, and many others to let your image go through the upscaling process and enhance its features without compromising the resolution and clarity.
Step 1: Image Preparation
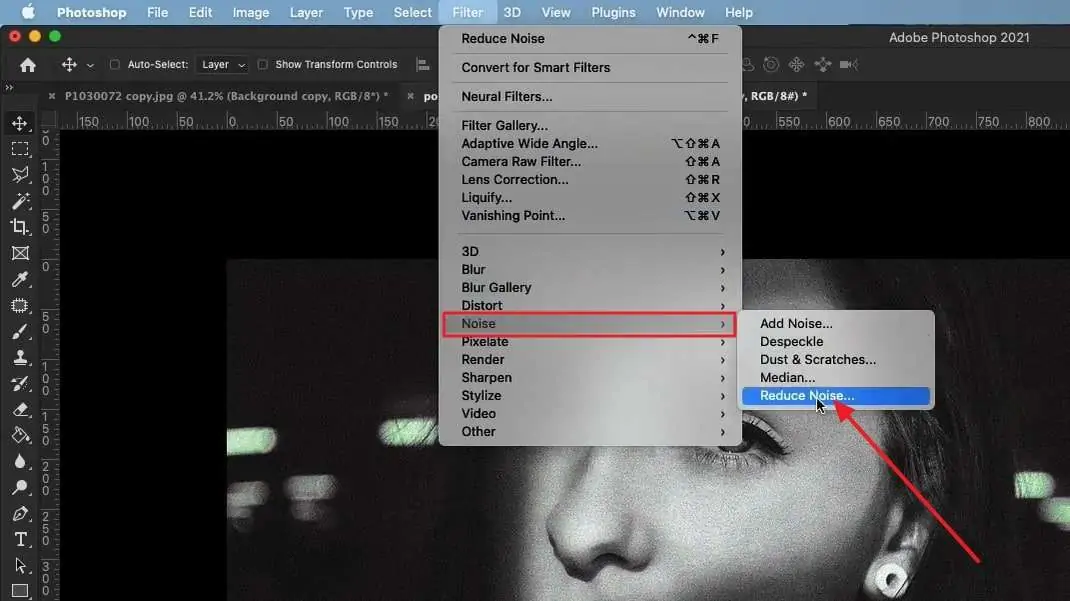
Start by analyzing the image to recognize any flaws or issues that might influence the quality of the ultimate result.
Utilize filters or tools to reduce any noise shown within the picture, like graininess or digital artifacts, which can degrade from the clarity of the upscaled version.
Attend to any obvious artifacts, like compression artifacts or sensor dust spots, that will be shown within the picture. These artifacts can misshape details and influence the viability of the upscaling process.
Correct any distortions within the picture caused by variables, including focal point aberrations or perspective twisting. Redressing these distortions guarantees that the upscaled image keeps up exact proportions and perspectives.
Assess and alter the image’s color balance, saturation, and contrast to guarantee optimal visual appeal and precision. Adjusting color issues before upscaling helps preserve the integrity of the colors in the final result.
Think of cropping the image to expel any superfluous or diverting components, focusing on holding imperative details and compositions.
This initial Editing can help optimize the upscaling process by decreasing the amount of interpolation required.
Step 2: The Zones Selection
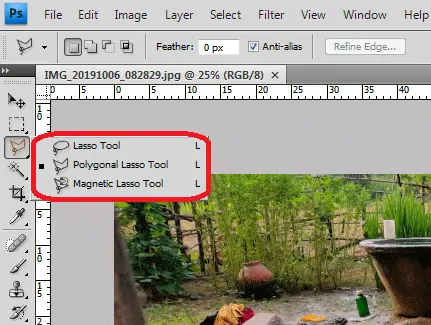
Analyze the image to decide on particular zones or regions that require upscaling. Focus on recognizing key components, such as critical details, textures, or objects that should be protected or improved.
Prioritize districts based on their noteworthiness or significance to the overall composition or message of the image. Bring more attention and resources to zones with basic details or central focuses.
Employ selection tools, like lassos, masks, or brushes, to absolutely define the boundaries of the chosen regions. Ensure precise choice to avoid including superfluous components or barring imperative details.
Tune the selection to refine the boundaries and guarantee that, as it were, the required districts are included for upscaling. Utilize adjustment tools to alter the choice as required, considering variables like feathering or edge refinement.
Survey the chosen regions to affirm their precision and suitability for upscaling. Before continuing, use preview modes or overlays to imagine the chosen regions and make any vital alterations.
Approve the selection against the initial picture to guarantee consistency and alignment with the aiming objectives of the upscaling process. Confirm that the chosen locales precisely speak to the required zones for improvement.
Step 3: Choosing Algorithms
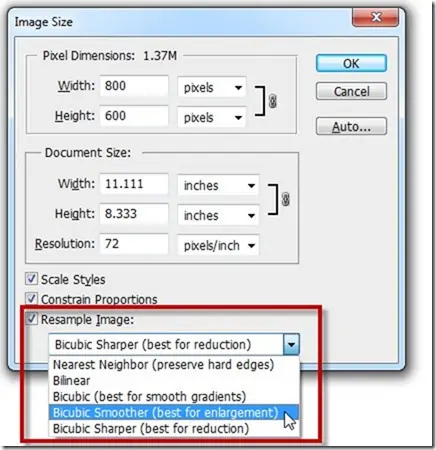
Evaluate different upscaling algorithms accessible within the software or tools being utilized. Consider variables like image content, wanted yield quality, and computational assets.
Select the Nearest Neighbor algorithm for basic upscaling errands where protecting sharp edges and pixelation artifacts is satisfactory. This algorithm duplicates existing pixels to extend picture size.
Select Bilinear Interpolation for even upscaling with a moderate increase in computational complexity. The algorithm calculates new pixel values by equalling the colors of neighboring pixels.
Opt for Bicubic Interpolation for higher-quality upscaling with progressed edge conservation and smoother gradients. This algorithm employs cubic polynomials to introduce pixel values based on neighboring pixels.
Look into advanced upscaling algorithms according to machine learning, like deep learning models. These algorithms scrutinize image substance and designs to create high-quality, upscaled images with negligible artifacts.
Guarantee the chosen algorithm is consistent with the software or tools being utilized and underpins the required output format and resolution.
Perform preparatory tests with distinctive algorithms to assess their execution and decide the most appropriate choice for the particular image and necessities. Alter parameters as required to attain the specified developments.
Step 4: Algorithm Application
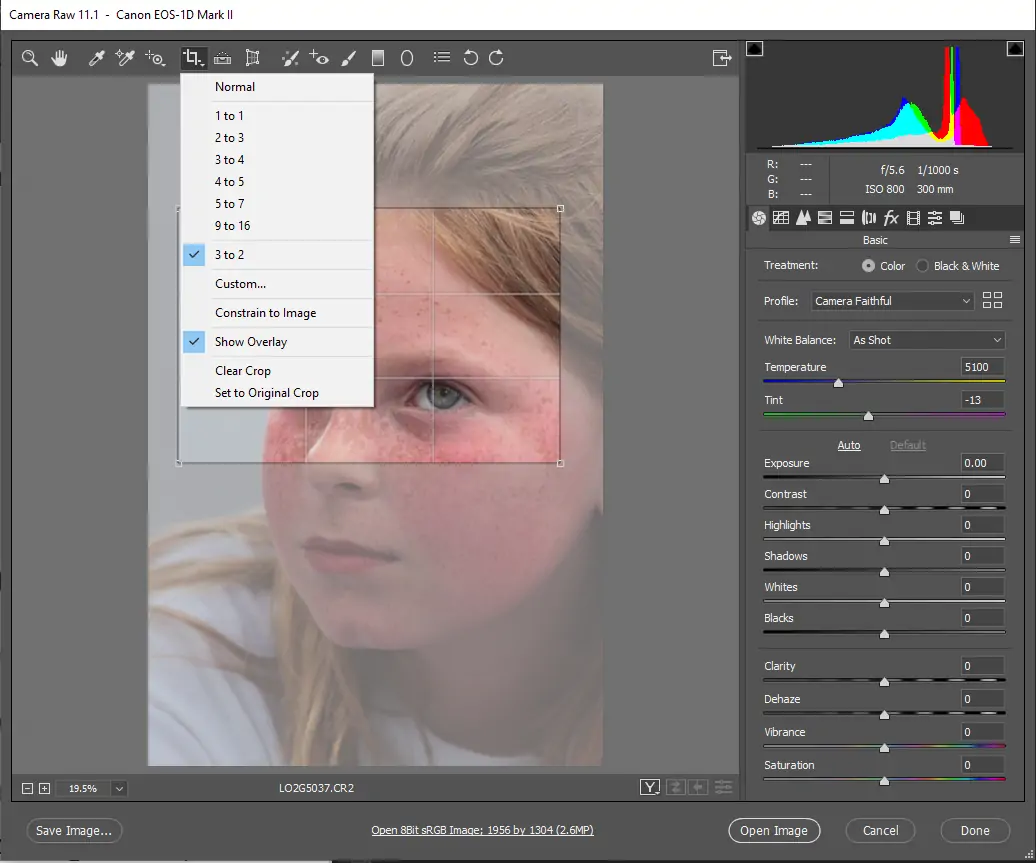
Execute the chosen upscaling algorithm to extend the resolution and estimate of the picture. Utilize the algorithmic settings to fine-tune the upscaling process concurring to particular prerequisites.
Utilize interpolation procedures to produce new pixels and fill within the gaps made during the upscaling process. This involves calculating pixel values based on neighboring pixels to preserve visual coherence and sharpness.
Alter parameters such as edge conservation and texture improvement to hold critical features while expanding resolution.
Reduce blurring, pixelation, or ringing effects that will emerge from the upscaling process. Regulate parameters related to noise diminishment and artifact suppression.
Screen the upscaling progress in real-time or use previews to survey the algorithm’s effect on the picture. Based on visual feedback, make vital alterations to parameters or settings to acquire ideal upshots.
You can apply the upscaling algorithm numerous times with shifting settings to get the specified level of improvement.
Perform careful quality checks on the upscaled image to guarantee that it meets the required guidelines in terms of clarity, sharpness, and overall visual mark.
Step 5: Tuning The Variables
Adjust the sharpness settings to upgrade the clarity and definition of edges and subtle elements within the upscaled image. Altering sharpness can help compensate for any softening impacts the upscaling process presents.
Add noise reduction strategies to decrease undesirable artifacts, like graininess or digital noise, within the upscaled image.
Assess and alter the color balance, saturation, and contrast of the upscaled picture to guarantee precise and dynamic colors. Adjusting color irregularities moves forward overall visual constancy and improves the aesthetic appeal of the picture.
Set contrast settings to progress the general tonal range and energetic range of the upscaled image. Altering contrast improves image profundity and dimensionality.
Tune surface options bring out inconspicuous subtleties and include authenticity to the image, particularly in ranges with complicated patterns or textures.
Ceaselessly see the upscaled image and compare it with the initial to assess the adequacy of alterations. Utilize side-by-side comparisons or overlays to survey changes and make further refinements as required.
Step 6: Final Reviewing
Double-check the precision of the chosen regions to guarantee they adjust with the aiming zones for upscaling. Audit the boundaries and contents of each chosen locale to confirm their significance and importance.
Compare the chosen regions with the initial image to affirm that fundamental details and components have been included for upscaling. Guarantee that no basic highlights have been ignored or prohibited during the choice process.
Assess the consistency of the chosen regions across the whole image to preserve coherence and balance. Guarantee that chosen ranges incorporate consistently with the rest of the picture and contribute to the prevailing composition successfully.
Refine boundaries, include or remove zones, or modify selections to progress the general quality and adequacy of the upscaling process.
Build up clear criteria or guidelines for approving chosen regions, considering components like significance, visual conspicuousness, and relevance to the image’s substance and message.
Conduct a last audit of the chosen districts to guarantee they meet the specified standards and destinations of the upscaling process.
Step 7: Image Export
Prior to upscaling, reinforce the first image file to protect the integrity of the source data.
Select the fitting file format for saving the upscaled image on aiming utilization and compatibility prerequisites. Incorporate JPEG, PNG, TIFF, and others, each providing distinctive compression levels and quality settings.
Set the required resolution for the upscaled image, agreeing to particular output prerequisites, like printing or digital display.
Alter quality settings like compression level or color depth to optimize the balance between file size and picture quality. Tune these settings to attain the required balance and guarantee ideal visual constancy.
Indicate the destination folder or area where the upscaled image will be saved. Arrange files efficiently to encourage simple get-to and management, particularly when working with different images or projects.
Use a reliable naming convention for the upscaled image file to guarantee clarity and organization. Incorporate important information such as project title, date, and version number for simple identification and following.
At last, save or export the upscaled picture using the chosen settings and parameters.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, image upscaling is a pivotal aspect of image enhancement that can equip photographers, graphic designers, and digital artists with the ease to maximize the size and resolution of photographs while maintaining quality. It is critical for all those domains where high-resolution images are in demand, such as print media, digital displays, and online venues. Image upscaling strategy stimulates professionals and enthusiasts to boost the grade and presentation of their visual content. With the ongoing refinements in technology and algorithm expansion, the image upscaling technique is also evolving and amplifying the infinite prospects for visual manifestation.



