How to Protect Digital Data in Healthcare
Strong security is crucial for healthcare data privacy. As cyber threats keep rising, healthcare administrations should follow best practices to protect their private information stored in internal systems. Nearly every major healthcare organization worldwide uses digital technologies, so everyone in the field is affected. Electronic health records are at higher risk of access by unauthorized people.
Here are some ways to handle existing threats and protect healthcare data.
Organize Healthcare Data
Maximize your healthcare data in a standardized format, utilizing the same file types, locations, folder naming conventions, and file naming standards. This makes it easier to search for data and can help automate security measures.
Educate Healthcare Staff
Human error remains the biggest threat to healthcare data security. Educate healthcare staff with security awareness training. Equip your staff with the knowledge to make the best decisions when handling patient data and use caution.
Utilize Secure Data Backups
Store encrypted copies of healthcare data in offsite and cloud backup locations. Ensure data is available in a data breach, system shutdown, or disaster. Test your backup systems periodically to verify data is stored accurately and as intended.
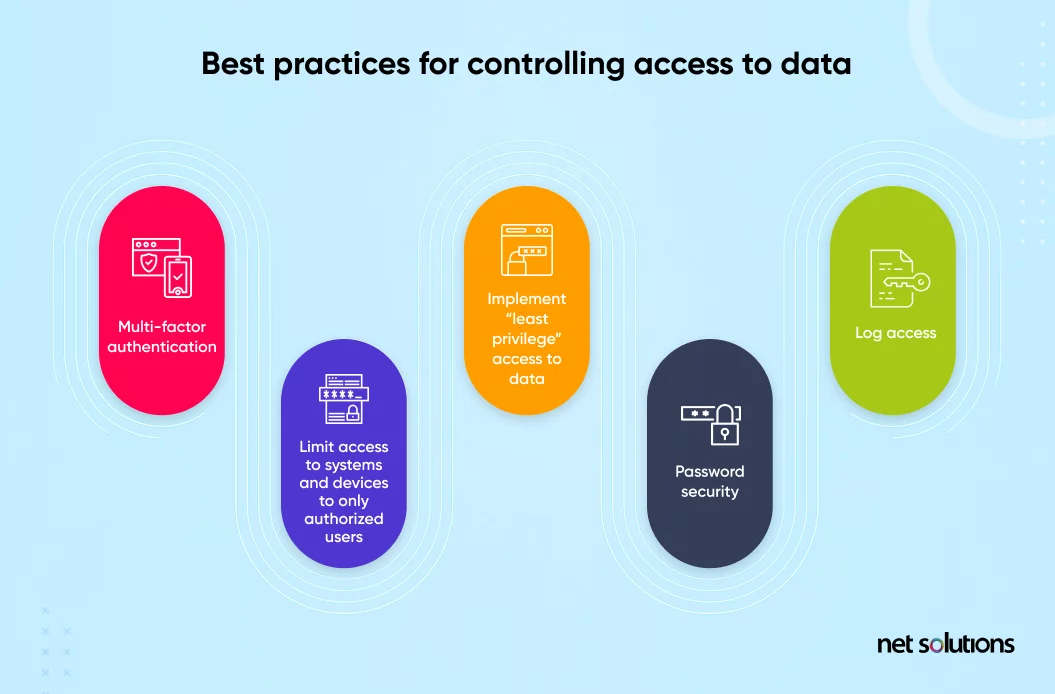
Implement Strong Access Controls
Only authorized personnel should have access to healthcare data. People should be provided with their account and user number to control, limit, and log exposure to sensitive information. Also, require multiple forms of verification for new devices, such as passwords and biometric data, for all users.
Monitor Data Usage in Real-Time
When you monitor data usage, you can identify and block risky or malicious data activity in real time. Data controls can be automated in many cases. This can help shut down potential breaches, such as web uploads or downloads, unauthorized email forwarding, copying to external drives, and printing.
Meet All Regulatory Requirements
Meet the strict regulatory requirements set by governments and industry regulators to protect user data. To this extent, never use patient data in ways not previously agreed upon by the patient. You should also use healthcare compliance software to manage regulatory requirements.
Restrict Access to Applications
Ensure healthcare data is carefully restricted, as it’s exposed to connected apps or software. Every app or software has vulnerabilities. The fewer apps or software healthcare records come into contact with, the better.
Device Management
Ensure the security of all computers, tablets, and mobile devices used to access healthcare data. This may entail preventing remote access or imposing restrictions that make some tasks harder.
Prioritize Mobile Device Security
Strong security measures are necessary to keep healthcare data safe on mobile devices. All settings should be correctly set up. Strong passwords should be enforced. If a device is lost or stolen, it should be wiped or locked remotely.
Monitor email accounts and attachments to avoid malware. Only allow applications that meet set criteria. Ensure mobile devices have the latest operating system and application updates.
Use End-To-End Encryption for Data Transfer
Implement end-to-end encryption across your communication channels to ensure patient data is secure during transfer and storage. This is necessary when exchanging records and information between healthcare professionals.
Data Encryption and Lockout Features
In addition to encryption, when data is transferred, it can also be encrypted at rest. When data is stored on servers or local devices, ensure it remains unreadable in case of a security breach.
Lock out accounts after a certain number of failed password attempts, preventing unauthorized software access.
Engage in Regular Safety Audits
Review and test security policies, procedures, and technologies around healthcare data storage and transfer. With each safety audit, you can identify vulnerabilities and make corrections.
Take Non-Essential Data Offline
If you have non-essential medical records, insurance information, and other details you don’t need accessible, remove them from your data center or storage center. When data is offline, it’s inaccessible to unauthorized parties.
Continuous Education for Staff
Provide staff with ongoing training and updates as data protection standards and protocols advance. Ensure they are updated with current best practices for protecting healthcare data.
Run Antivirus Scans Regularly
Use up-to-date antivirus software to scan your data and the computers that store or use it. Scan all endpoints for malware, ransomware, vulnerabilities, or indications of compromised access.
Establish an Incident Response Plan
If a security breach or suspicious activity is detected, have a plan. Designate an IT professional or team to manage and mitigate data breaches. The faster you act, the more likely data will be contained.



