How To Implement A Double-Keying System For High-Accuracy Data Entry
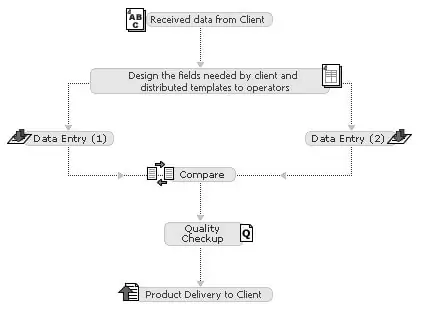
Businesses frequently struggle with data because even the best-organized teams can get overwhelmed by the operational constraints of daily tasks and the responsibilities of maintaining accuracy. The double key data input method, which provides unmatched precision and efficiency, is useful in this scenario. Double key data entry is an advanced approach which involves two separate data entry operators entering identical data, for instance, on different Excel spreadsheets. This dual-input method yields a much greater degree of accuracy since it is followed by a comparison phase to identify differences. This degree of scrutiny of the data entry process helps industries such as healthcare, finance, and research significantly, lowering the chance of human errors, ensuring that the final data set fulfils the highest possible grade of precision and accuracy. Within the widescale double-keying, the same documents are taken by two teams assigned by the project manager, who use the same procedure to digitize the content and produce two distinct files, which are comprised in the end to compose a flawless final input.
Step 1: Set Up The System
In the first place, you will have to set up a well-regulated data entry system for which you need to determine the type of data you need to capture. Characterize the input fields to confirm that they support the dual-entry function. For instance, the fields should have particular formats, drop-downs, and text fields to maintain uniformity.
Apply a framework that facilitates two independent data entry processes to execute. That will help prevent partiality and catch errors as soon as possible. The systems should be capable of forbidding the operators from seeing former entries, sustaining the integrity of the process.
Pick a software that holds up automated error detection, real-time validation, and double-keying. Organizations can utilize cloud-based solutions or dedicated database management frameworks according to their requirements.
Set different operators for both the 1st and 2nd passes. Keep the access under control so as not to get random overwrites or changes to the data that was previously entered. It makes sure that each data entry operation stays independent while lowering the risk of operating blunders.
Train the operators about data entry procedures, software utilization, precision, and expected outcomes; as well-trained personnel perform a vital part in reducing errors, it ensures efficiency in the following validation and error-resolving phases.
Step 2: Execute 1st Datta Entry
Assign the task of inputting the initial data set to an efficient operator who follows preset guidelines like proper formatting, character limit compliance, and entry verification before submission.
The operator personnel will enter data in the fields assigned to the software or database. The system is supposed to do standard validation checks, like verifying that the numeric field only has numbers and that the mandatory fields are not blank, which ensures the reduction of common errors.
The operators will have to utilize standardized dates, names and other formats to keep up conformity. Uniform data input will help minimize disparities between the 1st and 2nd phases. Moreover, auto-complete features, dropdown menus, and real-time validations help overall consistency.
After the 1st entry completion, the system will store data without permitting modifications. It will confirm that the 2nd data entry stays self-standing.
Now, as the 1st data entry is prepared, the second operator can proceed with the re-entry of data without gaining access to initial inputs. It will make sure that any inconsistencies are discovered during the comparison period.
Step 3: Execute 2nd Data Entry
This step needs to assign a different operator who had nothing to do with the 1st data entry operation. This operator will re-enter the data without getting biased or affected by the 1st data entry.
That operator will stick to the exact formatting patterns and validation rules employed by the 1st operator. The utilization of consistent data formatting, structured text inputs, and regulated conventions ensures minimum variations caused by varying entry styles.
Though the software employed for entry operation is supposed to provide real-time validation to check obvious errors, the system will not compare both entries at this stage to maintain the rectitude of the independent input.
After the 2nd entry is concluded, it will be saved separately in the system so that it stays unaltered till the automation process starts.
Step 4: Performing The Comparison
After the execution of both data entry passes, the system will perform an automated comparison operation. This process will review whether the two separately entered data conform to each other or contain disparities.
The system will inspect to find any mismatches between the 1st and 2nd data entries. In case any disparities are found, like incorrect spellings, digits, or missing fields will be flagged for a recheck. The detected inconsistencies may be listed in separate reports or colour-coded depending on the software you are using.
The advanced systems can provide ruled-based validation that can detect errors that are not so apparent, for instance, if there is some numeric field that contains some unrealistic value or a mailing address with a missing @ symbol.
To report all errors in detail, the system will assemble a report that displays side-by-side comparisons of the 1st and 2nd entries, aiding the reviewers in assessing the differences on the spot.
After the errors and inconsistencies are determined, the flagged data will be passed for review, setting the stage for the following step of manual error examination and correction.
Step 5: Resolving The Errors
In this phase, a well-trained supervisor will examine the flagged mismatches identified by the automated comparison reports. The reviewer will find out that the discrepancies are caused either by typographical errors, inaccurate data inputs, or formatting issues.
To precisely solve errors, the supervisor cross-matches the disputed entries with the original documents or sources. It is to make sure that corrections are based on facts, not assumptions.
The reviewer will rectify the incorrect data within the system while adhering to the standardized formatting guidelines.
Once the data is modified, the system can rerun a validation check to ensure that all errors are handled properly. If the reviewer still finds any remaining uncertainties, he or she can opt for some additional verification from the concerned crew.
After resolving all of the irregularities and errors, the modified data can be identified as verified. After the final assessment, correction and validation, it is time to store it and ensure that it is accessible easily.
Step 6: The Final Validation
Before proceeding with data storage, the site will conduct a reassuring validation check to confirm all issues are properly handled.
After that, the data is also manually checked, ensuring its relevancy with the business rules and other criteria and confirming that the data is applicable to operational goals.
After data validation is accomplished, the database will be locked so that it is protected from any unintentional modification. Moreover, the appropriate access controls are put in so that only authorized personnel can access or utilize the finalized data, minimizing the likelihood of unauthorized alterations.
In the end, the validated dataset can be stored in a secure dataset, data management systems, or any proper option, such as cloud storage, depending on the requirements of the organization.
Furthermore, a final report will be prepared that outlines errors, corrections and validation checks. This final auditing presents a coherent data entry precision and a direction for future reference.
Conclusion
To conclude, accurate and effective data entry tasks are encouraged in a well-designed workplace. With the correct configuration, mistakes could be minimized and output increased. The major advantage of double-keying data input is that it reduces errors and enhances efficiency. Having two teams can double accuracy for enterprises that handle a lot of documents and cannot afford to make any mistakes. By entering data twice and comparing the outcomes, mistakes could be identified early on, improving the precision and proficiency of the final data submission.