
How to Build a CRM System From Scratch: A Complete Guide 2024
Customer relationship management (CRM) software is essential for managing interactions with customers and prospects. Off-the-shelf CRM solutions may not fully address the unique needs of every business. Building a CRM from scratch allows complete control to tailor the system to your sales, marketing, and support workflows.
Understanding CRM Basics
Before searching for CRM development services, it’s important to understand key CRM concepts.
What is CRM?
CRM stands for customer relationship management. A CRM system consolidates customer and prospect data and interactions from across an organization into one place. This provides visibility into the entire lifecycle of relationships for more informed, personalized experiences.
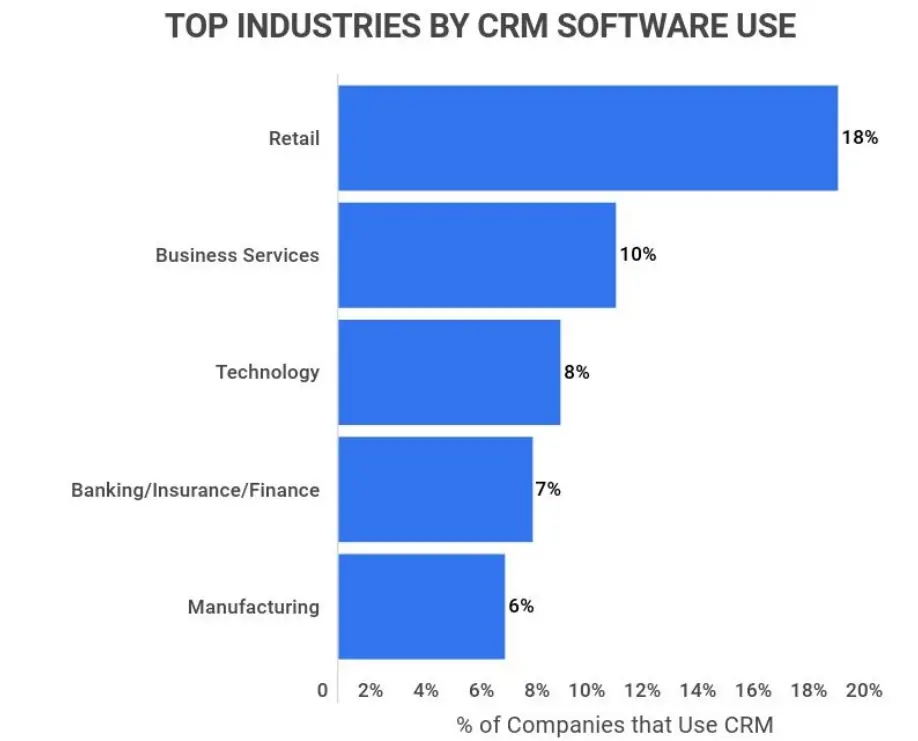
Specifically, a CRM centralizes all information regarding prospects and customers, including contact details, company information, interactions, sales opportunities, support cases, and more. This data empowers sales, marketing, and customer service teams to track better, manage, analyze, and nurture relationships for revenue growth and an excellent customer experience. In addition to retail, CRM systems are also widely used in business services and technology.
Core CRM Capabilities
Though CRMs can include many features, several core capabilities tend to be consistent:
Contact management: Organize key information on customers and prospects, such as name, title, company, contact info, etc. This includes the ability to segment contacts by various attributes to target communications and track metrics by customer type.
Activity tracking: Log emails, calls, meetings, notes, and more to record interactions. Activity histories provide insights into engagement levels over time and help continue conversations from where they left off.
Lead management: Define and track leads by scoring and routing them to sales reps. Lead definition, scoring methods, and automated nurturing workflows fuel pipeline growth.
Opportunity tracking: Manage deals through sales pipeline stages to forecast revenue. Advanced opportunity management drives win rates and deal sizes up.
Marketing automation: Send targeted emails, nurture leads, and measure campaign performance. Automated multi-channel campaigns convert more leads more efficiently.
Global demand for CRM solutions is being driven by the growing need for automated customer engagement, expanding the scope of digital operations, and improving customer experience and services.
Key Planning Steps Before Building a CRM
Carefully planning the build CRM from scratch process will set the project up for success. Rushing ahead without gathering requirements, mapping workflows, estimating resources needed, and getting buy-in from impacted teams will likely result in a solution that falls short or needs significant rework.
Define Requirements
Analyze current sales, marketing, and service processes to define concrete functionality requirements. Engage representatives from each team to understand needs and pain points.
Map Data and Model Workflows
Map all data needing capturing and diagram workflows for processes like lead assignment, deal progression, ticket handling, and campaigns. Accurately flowcharting steps and logic will enable automation later.
Prioritize Features
Distinguish must-have features for initial launch vs. nice-to-haves for later phases. Prioritize what’s critical for the first version.
Select Tech Stack and Estimate Timelines
Choose technologies for capabilities and development expertise. With scoping done, realistically gauge timelines and resources required.
Step-by-Step Guide On How to Build a CRM From Scratch
Once planning is complete, it’s time to build. Follow these key steps:
Design the Database
Structure the database that will organize and connect all the customers, pipelines, interactions, and other data needed for capturing. Properly designing schemas and relationships between tables and records at this foundational level is crucial for configuring what data can be stored, queried, and reported on later.
Common CRM tables may include contacts, companies, deals, products/services, interaction history, tickets, campaigns, and more. Define each field with appropriate data types and validation rules for value formats. Establish table relationships and junction records to mimic real-world connections.
Create Core Record Types
Establish the foundational record types to store key CRM data, like contact, deal, ticket, email activity, etc. Consider required fields, optional fields, relationships to other records, page layouts, and key actions for each record type. These building blocks empower capturing all needed data.
Build Key Workflows
Leverage the modeling done during planning to begin the automation of the workflows of the important processes. This can be advancement rules for deal stages, lead assignments, email sends, notifications, field updates and much more. Construct your processes with unique flow and conditions that fit your operations instead of forcing the operations into the mold of a standard platform.
Develop Role-Based Interfaces
Create interfaces, views, and operations appropriate for each role: sales, marketing, customer service, finance, etc. Support reps, for instance, may need different related record tabs, different focus on page layout, different actions, and navigation compared to sales reps. Developing UIs for personas is effective in terms of efficiency.
Incorporate Intelligence
Integrate artificial intelligence and automation capabilities to enhance certain areas of the CRM where relevant. Examples include contact data enrichment with supplemental demographic or firmographic details from business data providers, sentiment analysis on customer support case communications, deal scoring predictions and next best action recommendations for sales reps, and more.
Enable Mobility
Today’s workforce is mobile, so build responsive design and cross-platform support into the CRM solution from the start to allow accessing and managing records from anywhere. Consider how to build CRM native mobile apps on iOS and Android versus mobile-optimized web app experience. Offline access may also be beneficial for remote reps.
Ensure Data Security
Incorporate robust security protections, access controls and permissions to safeguard sensitive customer data. Support single sign-on integration with common identity providers. Enable encryption of sensitive fields and data transmissions. Authentication and authorization protocols must align with industry security standards.
Create Centralized Reporting
Develop reports and dashboards to surface key metrics and trends across the consolidated CRM data to inform strategy and operations. Track KPIs specific to different roles – like lead conversion rates for marketing or sales booking attainment for sales reps. Custom reports built on a unified data set provide complete visibility.
Allow Customization
Build CRM from scratch with settings, tools and options to empower admins and possibly end users to customize aspects like layouts, views, fields, workflows, branding, etc., to fit evolving needs post-launch. Customization tooling future proofs changing business requirements so teams can adapt the system over time versus requiring developer effort each time.
Integrate Other Systems
Connect and sync the CRM data with other surrounding systems like email marketing, billing, ERP, etc. Building APIs and integration middleware facilitates tying data across platforms for interoperability instead of siloed solutions.
Launching and Iterating On Your Custom CRM

Once the MVP build is complete, it’s gone time. But the work doesn’t end at launch.
Beta Test
Have team members pilot the platform with real data to surface any bugs or usability issues before launch. Gather feedback on what works well versus potential points of friction or confusion to address. Test with users who will be adopting the system to ensure it aligns with their workflows and expectations before officially rolling out.
Train Employees
Provide sufficient training resources and support to get sales, marketing and customer service teams adept at using and adopting the new system, whether through self-guided content, virtual sessions, or in-person workshops. Appoint department power users to continue assisting peers after initial training as the first line of support.
Migrate Data
Import relevant legacy customer, pipeline, and project data into the new CRM so it can be leveraged right away without building CRM from scratch. Data migration avoids losing institutional knowledge and allows teams to hit the ground running. Cleanse data to weed out duplicates or errors during migration.
Market to Customers
Promote the new customer portal and self-service capabilities to contacts to encourage adoption. Send onboarding emails introducing the functionality relevant to customers based on their relationship history.
Continuously Improve
Solicit ongoing end-user feedback about what parts of the CRM they find most and least valuable. Prioritize future enhancements that are aligned with current business objectives. Release regular updates to meet evolving needs versus stagnating at the first version. Building custom allows continuously aligning to strategy versus working within rigid off-the-shelf constraints.
Conclusion
So, how to create a CRM from scratch? Creating a tailored CRM solution involves a lot of planning that will ensure that it fits the needs of marketers, salespeople, and customer support agents. Adopt the best practices for design, development, and implementation to ensure that your CRM project will bring great results by improving customer insights and optimizing business processes. Continuously update to create value after the launch of the application. When implemented with the right vision and methodology, a custom CRM can be the key to customer relationship management.



